This report is also available as an Acrobat file.
Multimedia Presentations Workshop
Working Group 2 - Basic Environments
Chair: Philip Barker
Introduction
This group looked at the basic requirements for both developing and delivering multimedia presentations. Two main perspectives were considered:
- development - gathering material, creating video/audio clips e.t.c; and
- presentation - how difficult it is to take a presentation and use it elsewhere (e.g., compatibility problems with both software and hardware).
The group explored the idea of producing guidelines at two levels:
- advice for a presenter; and
- advice for departments buying and setting up multimedia presentation equipment
Discussions
Three separate strands for discussion were identified:
- Development - gathering, capturing, converting and developing multimedia resources and integrating them into a multimedia presentation
- Presentation - Problems associated with making a multimedia presentation at local and remote venues
- The characteristics of the delivery environment to enhance the use of multimedia presentations
Strand 1 - Development Issues
Many people are already using tool such as PowerPoint to generate text-based presentations, often to produce OHP transparencies, which are easy to use, portable and reliable, but often perceived as bland by students
Factors that influence the transitions from talk through talk and chalk to multimedia presentation.
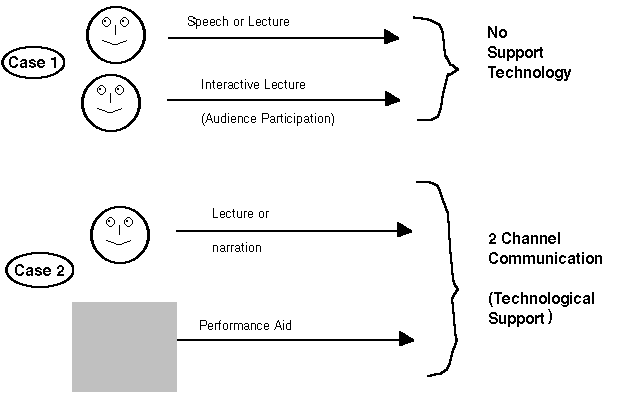
Types of presentation
Performance aids, such as OHP, slides and computer presentations, help with the delivery of a message by improving the communication bandwidth between the sender and recipient. A 3- channel system (2 aids) is just a variation of the basic model
The OHP is currently one of the most popular and widely available support aids, but anything that can be presented on celluloid can be emulated using electronic transparencies, and the group accepted that electronic presentation have the potential to be much superior to celluloid transparencies.
What is a multimedia presentations?
A multimedia presentation will contain some or all of the following resources:
text, sound, images of all sorts (including video/animation) and possibly some degree of interactivity.
These could be put together in various ways, for example on a CD-ROM , and delivered by computer, or may be published on multiple different and discrete media, such as video tape, audio tape, 35mm slides e.t.c.. The group felt they should really be consider the former as multimedia, and the latter they termed 'Polymedia', which it was felt lay outside the current discussions.
In other words, a multimedia presentation is:
human presenter + CD-ROM + Internet resources + digital resources
Gathering materials
There are a number of places multimedia materials can be found:
- Paper based resources - text/image
- Internet
- 3rd party resources
- self produced material
While some of these resources may be 'multimedia ready', i.e., they can be just imported into presentation tools, others will require some form of conversion e.g., conversion of analogue video or audio to a digital format. The resources required to do this will probably be centrally held, and use should be made of centres, such as the National Video Centre at Manchester, where there is equipment and experience available.
Issues Raised
- copyright problems
- quality audit
- finding resources and indexing of resources
Storage issues
- portability of basic resources (CD/tape streamer/portable hard disk/network)
- portability of presentation (CD/network)
- large amount of storage required during development of a presentation
Editing Issues
- a range of tools should be provided and supported
- tools vary in sophistication
- institutional services
- need for support units
- institutional training
- affect of the enthusiasm factor
Strand 2 - Presentation
The main issues raised under this heading related to delivery environment issues such as:
- resident software/hardware compatibility
- hardware suitability
- projection facilities
- local technical support
- lecterns for portables
- no trailing cables
Strand 3 - Lecture Room Issues
This strand looked at the physical requirements of lecture rooms. It is important that any audio- visual equipment does not block the view of the audience. For example a large dat projector located at the front of a small seminar room can block the view of many of the audience in the central part of the room. Consequently back projectors or ceiling projectors would be the preferred method.
The presenter should have full remote control facilities. This should include a remote control mouse, so that he/she is not tied to the computer. Lights should also be controlled remotely, either by lecturer or technician. Ideally all equipment would be effectively hidden from the audience, but where equipment is present there should be no trailing wires, which are not only distracting, but also present a health and safety risk.
Group Recommendations
Strand 1 - Developing
- Readily available equipment for converting analogue resources to digital
- Provide appropriate mechanisms for converting digital resources between different formats
- Adequate digital storage media such as high capacity portable hard drives and recordable CD
- Appropriate network infrastructure to facilitate exchange of digital resources and delivery within the organisation
- Appropriate guidelines for copyright observation with respect to utilising other peoples' resources
- Encouraged to share resources both with respect to equipment and intellectual material
- Support services for multimedia development
- Provide appropriate standardised development tools for use by staff
- Provision of training and support for staff to create their own material
- Institutional recognition of using multimedia teaching techniques and producing multimedia
- Guidelines about how individuals should go about developing (incrementally) multimedia presentations
Strand 2 - Presenting
- Host institution should ensure the operability and serviceability of equipment
- Technical support available to presenter
- Guidelines for the creation of a multimedia delivery box for presenters to use
- Minimum standard for presentation equipment:
screen/resident PC/audio support/ projection equipment/ remote mouse
Strand 3 - Lecture Theatre Provision
- Layout of equipment should not block viewers
- Automatic light dimming (remote)
- Cables hidden (health and safety)
- Network connection
- Telephone socket
- Information sheet describing hardware and software available including details of available players
- VCR+monitor, so ordinary videos can be played


Graphics Multimedia
Virtual Environments Visualisation
Contents






